PR-117 "PeerNets: Exploiting Peer Wisdom Against Adversarial Attacks" Review (2019 ICLR)(Adversarial Attack)
PR-117 "PeerNets: Exploiting Peer Wisdom Against Adversarial Attacks" Review (2019 ICLR)(Adversarial Attack)
1. Citations & Abstract 읽기
Citations : 2022.1.2 기준 36회
저자
Jan Svoboda - USI, Switzerland, NNAISENSE, Switzerland
Jonathan Masci - NNAISENSE, Switzerland
Federico Monti - USI, Switzerland, Imperial College London
Michael M. Bronstein - USI, Switzerland, Intel Perceptual Computing, Israel, Imperial College London, Fabula AI, UK
Leonidas Guibas - Stanford University, USA
Abstract

Deep Learning 시스템은 우리들의 삶의 많은 부분에서 보편화되었다. 불행히도, 이런 시스템들은 adversarial attack에 취약하여 잠재적인 불법 사용에 취약하다는 것이 밝혀졌다. adversarial attack에 강건한 DNN을 설계하는 것은 이런 시스템을 더 넓고 다양한 application(예) 자율주행)에서 안전하고 효율적으로 활용할 수 있게하는 근원적 단계이지만 더 중요한 것은 존재하는 기존에 존재하는 패러다임에서 미미하게 쌓아가는 것(?)보다 새로운 계산 패러다임에서 새롭고 더 진보된 아키텍처를 설계하는데 필요한 단계이다. 이 논문에서 우리는 PeerNets를 소개한다. 이는 고전적인 Euclidean conv와 graph conv를 번갈아 사용하여 peer sample의 그래프에서 정보를 활용하는 새로운 conv 네트워크이다. 이는 잠재 특징들이 그래프에 의해 유도된 전역 구조에 따라 조건화되는 모델에서 non-local 전역 전파의 형태를 초래하는데 이는 기존 구조 대비 정확도는 거의 떨어지지 않으며 화이트 박스 및 블랙 박스 adversarial attack에 최대 3배까지 강건하다.
unlawful 불법의
marginally 아주 조금, 미미하게
harness 이용하다, 활용하다.
2. 발표 정리
공식 논문 링크
https://openreview.net/forum?id=Sk4jFoA9K7
PeerNets: Exploiting Peer Wisdom Against Adversarial Attacks
Deep learning systems have become ubiquitous in many aspects of our lives. Unfortunately, it has been shown that such systems are vulnerable to adversarial attacks, making them prone to potential...
openreview.net
https://arxiv.org/abs/1806.00088
PeerNets: Exploiting Peer Wisdom Against Adversarial Attacks
Deep learning systems have become ubiquitous in many aspects of our lives. Unfortunately, it has been shown that such systems are vulnerable to adversarial attacks, making them prone to potential unlawful uses. Designing deep neural networks that are robus
arxiv.org
Presentation Slide
PR-117: PeerNets: Exploiting Peer Wisdom Against Adversarial Attacks
- Title: PeerNets: Exploiting Peer Wisdom Against Adversarial Attacks - Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/1806.00088 - Video: https://youtu.be/VQsG_Yk9KuQ Taekmin K…
www.slideshare.net
Contents
Adversarial Attack은 의료, 자율 주행 등에서 위험하게 사용될 가능성이 존재
Explaining and Harnessing Adversarial Examples (ICLR 2015)
https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6572
Explaining and Harnessing Adversarial Examples
Several machine learning models, including neural networks, consistently misclassify adversarial examples---inputs formed by applying small but intentionally worst-case perturbations to examples from the dataset, such that the perturbed input results in th
arxiv.org
https://tantara.medium.com/adversarial-attack-part-1-a830ec92acde
Adversarial Attack: Part 1
최근 삼성 SDS의 사이다(SAIDA)팀이 스타크래프트 AI 대회에서 1등을 차지했습니다. 플레이 영상을 보면 꽤나 높은 수준이고 실제로 많은 게이머들이 이기기 힘든 실력이라고 합니다.
tantara.medium.com
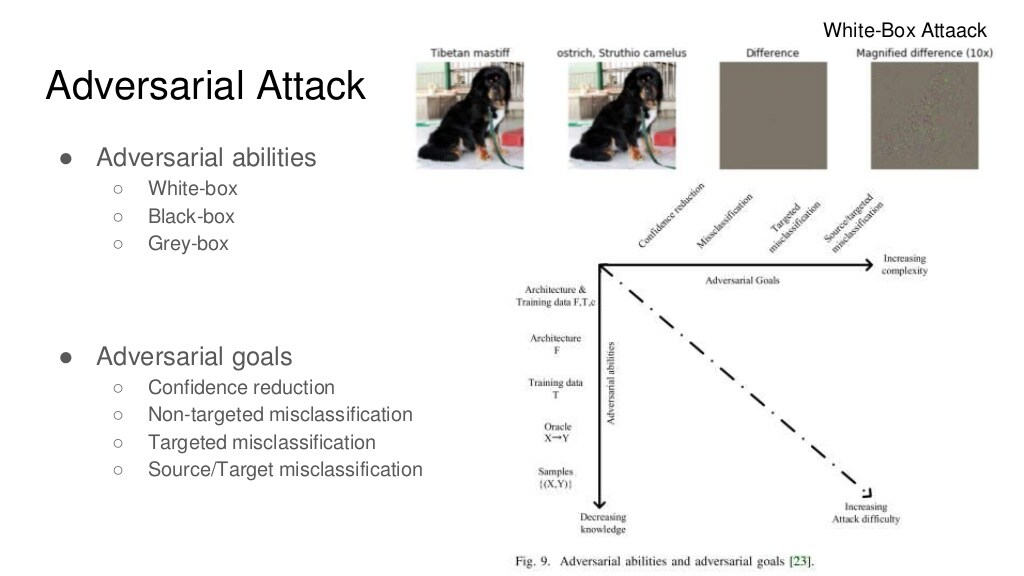
Adversarial abilities
White-box: 타겟 AI에 대해 모두 알고 있는 상황. 예를 들어, 딥러닝의 구조, Weight, Optimizer 등
Black-box: 타겟 AI의 입력과 그 출력만 확인 가능한 상황
Grey-box: White-box와 Black-box의 중간 단계
Adversarial goals
1) Confidence reduction
clasifier softmax 결과값을 낮추는 방향으로 adversarial example을 만드는 것
2) Non-targeted misclassifcation
정답이 아닌 어떤 class로 분류했으면 하는 것
3) Targeted misclassification
원하는 target으로 misclassification하는 것
4) Source/Target misclassification
source에 따라 target을 마음대로 control. 가장 어려운 문제
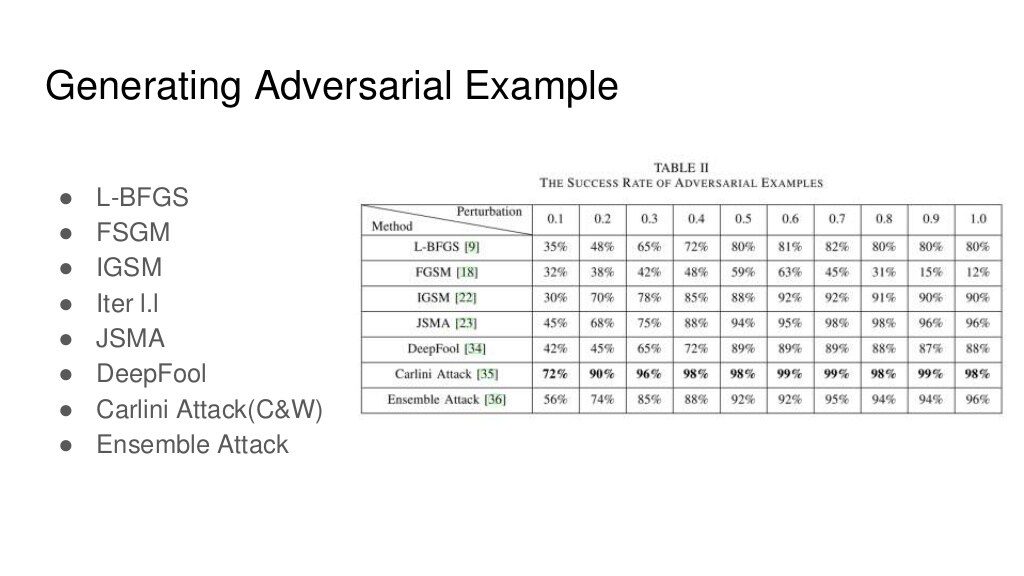
noise 강도 perturbation

Adversarial Example을 막는 방법
Adversarial Training / Detection / Defensive Distillation
목표
원본 모델 네트워크에 영향을 적게 주는 것
모델 스피드와 정확도 유지
Adversarial Example 방어하고자 하는 target에 대해서만 진행
Related Work 중 가장 흥미있는 것
One pixel attack for fooling deep neural networks(2017)
한 픽셀의 변경만으로 NN을 속일 수 있다는 논문
https://arxiv.org/abs/1710.08864
One pixel attack for fooling deep neural networks
Recent research has revealed that the output of Deep Neural Networks (DNN) can be easily altered by adding relatively small perturbations to the input vector. In this paper, we analyze an attack in an extremely limited scenario where only one pixel can be
arxiv.org
Overview
1) Use non-local forward propagation
GCN (Graph Convolutional Networks)을 활용하여 Adversarial Attack에 강건한 모델 설계
2) Result
- acc 하락은 미미함과 동시에 강건함은 3배까지 향상
- Strong Regularization Effect - Peer Regularization
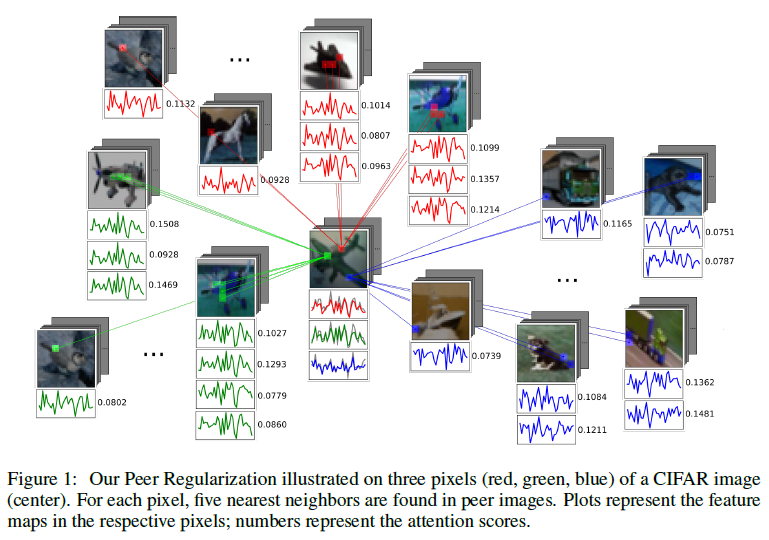
Input Image에서 비슷한 distribution인 다른 이미지들
sampling된 것들을 weighted sum
noise가 들어와도 강건함

social 망, 분자식, 지도 등 Graph 형태로 표현이 가능
Convolution도 Graph 형태로 표현 가능
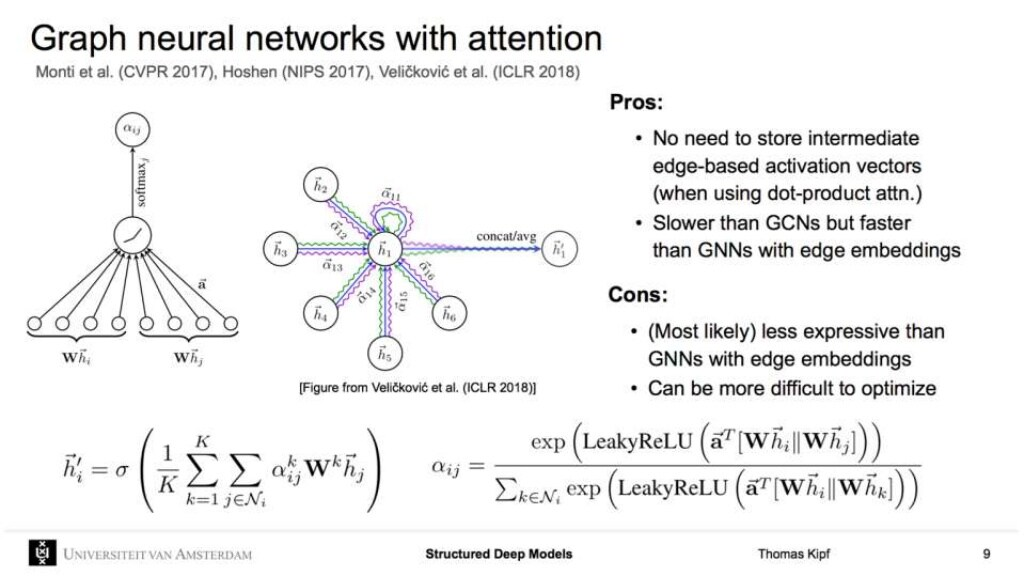
다른 가중치를 활용해서 더해주는 것 GNN with attention = GAN (Graph Attention Network)
제약, 분자, 화학식 사용에 GNN이 많이 활용
Peer Regularization
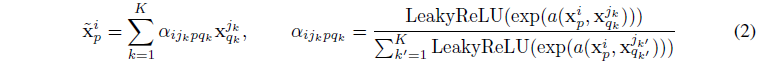
$x_p^i$ : i번째 image, p번째 pixel
주변 neighbor의 weighted sum
가중치 $\alpha$ : softmax 결과
Peer Regularization
neighborhood 설정 : 전체 or 일부 sample
일부만 sampling하여 weighted sum을 진행 -> 전체 계산량 감소
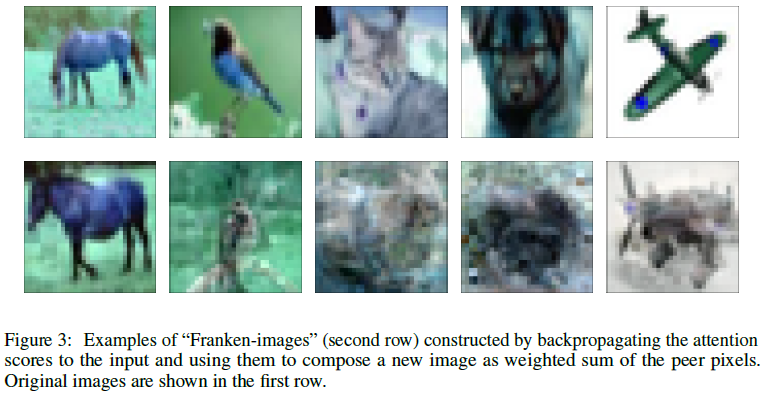




첫 행 : 원본
두번째 행 : Neighborhood Weighted sum 결과
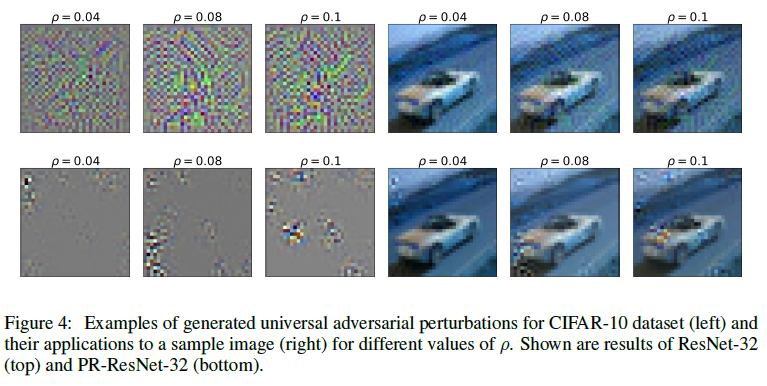
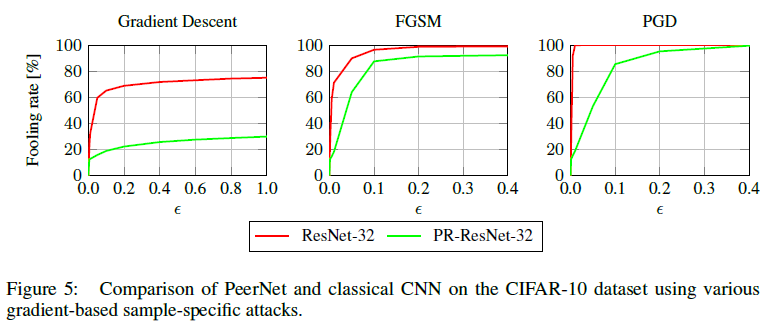
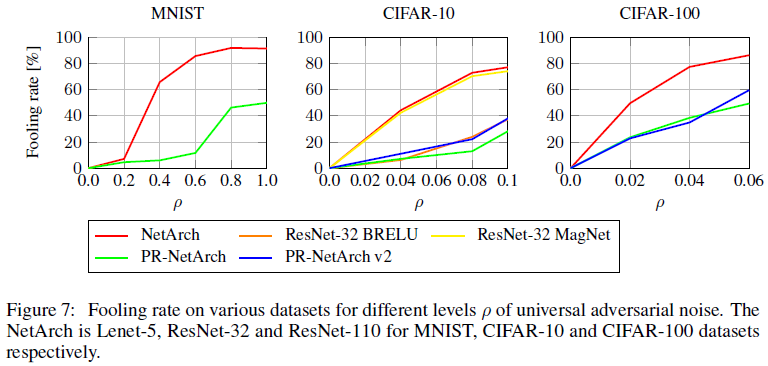
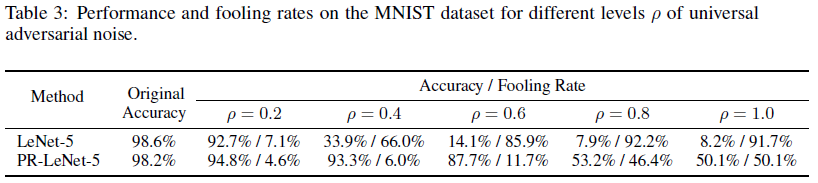

Feature map depth 2배로 키워서 PR Level 사용 시 acuuracy drop이 감소
참조
GitHub
https://github.com/tantara/PeerNets-pytorch
GitHub - tantara/PeerNets-pytorch: A pytorch implementation of 'PeerNets: Exploiting Peer Wisdom Against Adversarial Attacks'
A pytorch implementation of 'PeerNets: Exploiting Peer Wisdom Against Adversarial Attacks' - GitHub - tantara/PeerNets-pytorch: A pytorch implementation of 'PeerNets: Exploiting Peer Wi...
github.com
블로그
https://tantara.medium.com/adversarial-attack-part-1-a830ec92acde
Adversarial Attack: Part 1
최근 삼성 SDS의 사이다(SAIDA)팀이 스타크래프트 AI 대회에서 1등을 차지했습니다. 플레이 영상을 보면 꽤나 높은 수준이고 실제로 많은 게이머들이 이기기 힘든 실력이라고 합니다.
tantara.medium.com
https://tantara.medium.com/adversarial-attack-part-2-peernets-fd5ff62818a1
Adversarial Attack(Part 2): PeerNets
지난 튜토리얼(Part 1)에 이어서 방어에 대해서 간략히 다루고 이 튜토리얼의 핵심인 논문 PeerNets: Exploiting Peer Wisdom Against Adversarial Attacks의 리뷰를 진행하겠습니다.
tantara.medium.com
https://arxiv.org/abs/1503.02531
Distilling the Knowledge in a Neural Network
A very simple way to improve the performance of almost any machine learning algorithm is to train many different models on the same data and then to average their predictions. Unfortunately, making predictions using a whole ensemble of models is cumbersome
arxiv.org






